Fungal Acne Treatment: Unlocking the Secrets to Radiant Skin
If you've been struggling with stubborn breakouts that just won't seem to go away, you might be dealing with fungal acne. Unlike traditional acne, fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin. But don't worry, because in this article, we will explore the best treatments for fungal acne, what triggers it, and how to treat it from the comfort of your home.
What is the Best Treatment for Fungal Acne?
The best treatment for fungal acne often includes the use of antifungal agents. Here are some effective ways to combat this type of acne:
- Antifungal Creams: Topical antifungal creams containing active ingredients like ketoconazole or ciclopirox can help target and eliminate the fungal overgrowth causing acne.
- Natural Remedies: Natural remedies, often derived from plant-based or organic sources, can offer a more holistic and gentle alternative for those seeking to address fungal acne without the potential side effects of pharmaceutical options.
- Cleansing: A gentle cleanser with salicylic acid can help unclog your pores and remove dead skin cells. Be sure to avoid harsh or overly drying products, as they can exacerbate the condition.
- Antifungal Shampoos: If your fungal acne is affecting your body or scalp, using an antifungal shampoo containing ketoconazole can be beneficial. Make sure to let the shampoo sit for a few minutes before rinsing.
- Prescription Medications: In more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe oral antifungal medications like fluconazole. These are typically used when topical treatments haven't yielded satisfactory results.
What Can Trigger Fungal Acne?
Understanding what can trigger fungal acne is essential to prevent future outbreaks. Some common triggers include:
- Humid Environments: Fungi thrive in moist environments. Living in a humid climate or excessive sweating can encourage the growth of Malassezia yeast, leading to fungal acne.
- Occlusive Skincare Products: Using heavy, oil-based skincare products can trap moisture and create an ideal environment for fungal overgrowth. Opt for non-comedogenic products.
- Antibiotics: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of skin flora, making it easier for Malassezia yeast to overgrow.
- Tight Clothing: Wearing tight, non-breathable clothing can trap sweat and heat, which contributes to fungal acne on the body.
How to Treat Fungal Acne Naturally
While prescription medications can indeed be highly effective in treating fungal acne, it's worth noting that some individuals prefer to explore natural remedies as a gentler or complementary approach to managing this skin condition. Keep in mind that natural treatments may be less effective than medical interventions. Here are some natural approaches to consider:
- Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal and antibacterial agent. You can dilute tea tree oil with carrier oil (like coconut or jojoba oil) and apply it to the affected areas. Be cautious with tea tree oil, as it can be harsh on the skin if not properly diluted. Perform a patch test first to check for sensitivity.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Apple cider vinegar has antifungal properties and may help control Malassezia growth. Mix one part apple cider vinegar with one part water, and use a cotton ball to apply it to the affected areas. Rinse it off after a few minutes.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. Apply a thin layer of pure aloe vera gel to the affected areas to help calm inflammation and discomfort.
- Coconut Oil: Some individuals find that using coconut oil as a moisturizer can be helpful. Coconut oil has natural antifungal properties, but it can be comedogenic for some people, so use it sparingly.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a gentle, pH-balanced cleanser to keep the affected areas clean. Avoid harsh or abrasive cleansers, as they can irritate the skin.
- Probiotics: Consuming probiotics through foods like yogurt or dietary supplements may help support a healthy balance of microorganisms on the skin. A balanced microbiome can potentially discourage fungal overgrowth.
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing your intake of sugary and high-glycemic foods may help manage fungal overgrowth. A balanced diet can support skin health.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can exacerbate skin conditions. Engaging in stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or exercise may help keep stress levels in check.
- Stay Dry and Cool: Avoid tight clothing and stay in climate-controlled environments to minimize sweating and humidity, which can worsen fungal acne.
How Can I Treat Fungal Acne at Home?
While consulting a dermatologist is always recommended for severe cases, you can also take several steps to treat fungal acne at home:
- Cleanse Gently: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to wash your face and body. Avoid harsh scrubs or excessive exfoliation, as this can irritate the skin.
- Topical Antifungals: Over-the-counter antifungal creams or lotions can help clear up mild cases. Apply them as directed on the packaging.
- Hygiene: Ensure you're keeping your skin and clothing clean. Shower after workouts, and wear loose, breathable clothing.
- Diet: Some people find that reducing sugar and high-glycemic foods in their diet can help improve their skin.
How Do I Know if My Acne is Fungal?
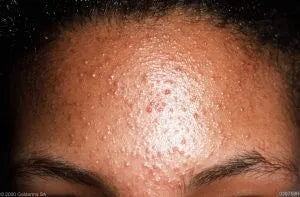
Distinguishing fungal acne from traditional acne can be challenging since the symptoms often overlap. However, some key indicators of fungal acne include:
- Tiny Bumps: Fungal acne usually appears as tiny, uniform, itchy bumps without blackheads or whiteheads.
- Uniform Distribution: These bumps are often evenly distributed, typically on the chest, back, and shoulders.
- Itching: Fungal acne is known for causing intense itching.
- Response to Antifungals: If your symptoms improve after using antifungal products, it's a strong indicator that you're dealing with fungal acne.
Fungal Acne Medication Side Effects
While treating fungal acne with antifungal medications can be effective, it's essential to be aware of potential side effects. The severity and occurrence of side effects can vary from person to person. Here are some side effects associated with commonly used fungal acne medications:
Topical Antifungal Creams:
- Skin Irritation: Some individuals may experience mild skin irritation, redness, or burning at the application site. This is usually temporary and can often be managed by reducing the frequency of application.
- Dryness: Antifungal creams may cause dry skin. It's important to use a moisturizer to counteract this effect and maintain skin hydration.
- Allergic Reactions: While rare, some people may develop an allergic reaction to the ingredients in the antifungal cream. If you experience swelling, severe itching, or hives, discontinue use and seek medical attention.
Oral Antifungal Medications:
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Oral antifungal medications can occasionally cause stomach discomfort, nausea, or diarrhea. Taking the medication with food can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Liver Function: In some cases, oral antifungals can affect liver function. Regular monitoring of liver enzyme levels is typically recommended during treatment, especially with long-term use.
- Drug Interactions: Antifungal medications may interact with other medications you are taking. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are using to prevent potential drug interactions.
It's important to note that most people do not experience severe side effects when using fungal acne medications. However, in some cases, the benefits of treating fungal acne may outweigh the potential side effects. Remember that these side effects are general guidelines and may not cover all possible reactions.
Preventing Fungal Acne Naturally
Preventing fungal acne naturally involves adopting specific habits and lifestyle changes that help maintain healthy skin and reduce the likelihood of Malassezia yeast overgrowth. Here are some natural ways to prevent fungal acne:
- Proper Hygiene:
- Regular Cleansing: Use a gentle, pH-balanced cleanser to wash your face and body. This helps remove excess oil, dirt, and sweat that can contribute to fungal acne.
- Shower After Sweating: If you've been sweating, especially after workouts, shower as soon as possible to prevent sweat from clogging your pores.
- Choose Breathable Fabrics:
- Opt for clothing made from natural, breathable fabrics like cotton. Avoid tight, non-breathable clothing that can trap heat and moisture, creating an environment conducive to fungal growth.
- Dietary Adjustments:
- Limit Sugar: Reducing your sugar intake can help prevent fungal overgrowth. High-sugar diets can promote yeast growth, exacerbating fungal acne.
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables into your diet. These foods promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which may indirectly help maintain skin health.
- Skincare Products:
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Use non-comedogenic skincare products that are less likely to clog pores and promote fungal acne.
- Tea Tree Oil: Some individuals find that incorporating a diluted tea tree oil solution into their skincare routine can help manage fungal acne. However, it's essential to patch-test and use it with caution, as it can be irritating for some people.
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Manage Stress: High stress levels can weaken your immune system and potentially contribute to skin issues. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough sleep to allow your body to rest and recover, promoting overall skin health.
- Limited sun exposure may be beneficial, as sunlight can have an inhibitory effect on Malassezia yeast. However, always wear sunscreen to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water to maintain skin hydration and overall health. Proper hydration can help your skin function optimally.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliation:
- While exfoliation is important, overdoing it can irritate the skin and disrupt its natural barrier. Opt for gentle exfoliation methods and avoid harsh scrubs.
It's important to remember that while natural prevention methods can be effective, they may not completely replace prescribed treatments if you have a severe fungal acne condition. By incorporating these natural prevention strategies into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of fungal acne and maintain clear, healthy skin.