Blackheads: Exposed
Blackheads are a common skin issue that can be both frustrating and bothersome. They often make an unwelcome appearance on our faces, affecting our skin's appearance and our confidence. We’ll delve into the world of blackheads, answering your questions about what they are, how they differ from whiteheads, their causes, natural treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What Are Blackheads?
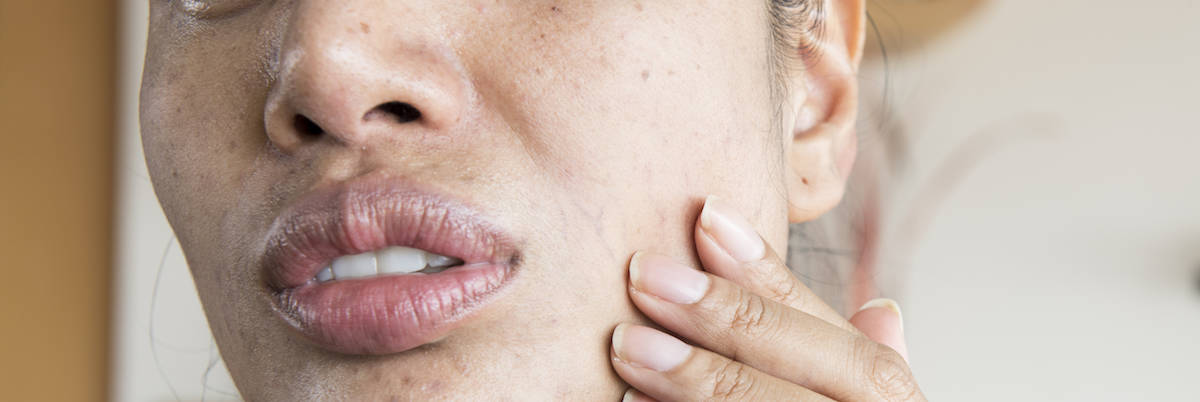
Blackheads are a common type of acne. They are small, dark-colored bumps that appear on the skin, often on the face, neck, chest, and back. Blackheads are considered open comedones, which means the pores where they form are exposed to air. This exposure to air causes the trapped sebum (skin oil) and dead skin cells within the pore to oxidize, resulting in the dark or grayish coloration that gives blackheads their name.
Unlike whiteheads, which are closed comedones with a white or yellowish appearance, blackheads have open pores, making them distinct in appearance. They are a result of clogged hair follicles, typically caused by excess sebum production, the accumulation of dead skin cells, and bacterial activity in the hair follicles. Understanding the causes and proper management of blackheads is essential for maintaining clear and healthy skin.

Blackheads vs. Whiteheads
Blackheads and whiteheads are both acne types but differ in their appearance and characteristics. Blackheads have open comedones with pores exposed to air, leading to their dark or grayish color, while whiteheads have pores sealed, resulting in a white or yellowish appearance.
Causes of Blackheads
Understanding the underlying causes of blackheads is essential for effective management. The main contributors include:
- Excess Sebum Production: Overproduction of sebum, the skin's natural oil, can clog hair follicles, contributing to blackhead formation.
- Accumulation of Dead Skin Cells: The buildup of dead skin cells on the skin's surface can mix with sebum and block hair follicles.
- Bacterial Activity: Bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, can thrive in clogged hair follicles, leading to inflammation and the development of blackheads.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and other life stages can increase sebum production, making individuals more susceptible to blackheads.
- Certain Skincare Products: The use of certain skincare products, especially those that are oil-based or comedogenic, can exacerbate blackhead formation.
Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and prevention of blackheads.
What Triggers Blackheads?
Various factors can trigger blackhead breakouts, including:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can lead to an increase in sebum production, making the skin more prone to blackheads.
- Excessive Sweating: High levels of sweat, especially in warm and humid environments, can contribute to clogged pores and the formation of blackheads.
- Diet: Diets high in sugary and processed foods may trigger inflammation and affect sebum production, potentially worsening blackheads.
- Improper Skincare: Using harsh or inappropriate skincare products, or failing to maintain a consistent skincare routine, can contribute to blackhead development.
- Excessive Stress: High-stress levels can stimulate the body to produce more sebum, contributing to clogged pores and the formation of blackheads.
- Heavy Makeup: Using heavy or comedogenic makeup products that clog pores can lead to the development of blackheads.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to producing more sebum, making them more susceptible to blackheads.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollution, certain chemicals, and high levels of humidity can contribute to blackhead formation.
It's important to be aware of these triggers and take steps to manage them, especially if you are prone to blackheads. A proper skincare routine and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent and manage blackheads effectively.
Do Blackheads Turn Into Pimples?
Blackheads do not typically turn into pimples. While they are both types of acne, blackheads are open comedones, and pimples are typically inflammatory papules or pustules. However, if blackheads become inflamed or infected, they can potentially develop into pimples.
Is it OK to Squeeze Blackheads?
Squeezing blackheads may seem tempting, but it's generally not recommended. Squeezing can lead to infection, scarring, and further irritation. It's best to opt for safe and effective treatments.
Natural Treatment Options
Treating blackheads naturally involves using natural ingredients to help manage and reduce these blemishes. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to treat blackheads effectively:
- Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine: Gently cleanse your face twice a day with a mild, non-comedogenic (won't clog pores) cleanser. Avoid scrubbing the affected area vigorously, as it can worsen inflammation.
- Exfoliate Regularly: Use a gentle exfoliant 2-3 times a week to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores. Be cautious not to over-exfoliate, as this can exacerbate the problem.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm, damp compress to the affected area can help open pores and promote natural drainage. Gently press the warm compress against the blackheads for 5-10 minutes, then carefully cleanse the area.
- Avoid Touching: Avoid picking, squeezing, or touching blackheads, as this can introduce bacteria and lead to infection and scarring.
- Avoid Comedogenic Products: Use non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) skincare and makeup products to prevent further clogging of pores.
- Moisturize: Even if you have oily or acne-prone skin, it's important to use a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated.
- Sun Protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin from UV damage, which can worsen acne.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit consumption of dairy and sugary foods, as they may exacerbate acne in some individuals. Get regular exercise and manage stress, as both can have an impact on skin health.
- Patience: Consistency is key. It can take time for treatments to show results, so be patient and stick to your routine.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing blackheads is often more effective than treating them. It involves adopting a proactive skincare routine and making lifestyle adjustments. Here are some tips to help you prevent blackheads:
- Cleanse Regularly: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to wash your face twice a day (morning and night). Cleansing helps remove excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells.
- Exfoliate: Use a mild exfoliant containing salicylic acid or glycolic acid 2-3 times a week. Exfoliation helps keep pores clear by removing dead skin cells.
- Moisturize: Even if you have oily skin, it's important to use a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to maintain skin hydration and prevent excessive oil production.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and makeup products labeled as "non-comedogenic" to minimize the risk of clogged pores.
- Sun Protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin from UV damage. Some acne treatments can increase sensitivity to the sun.
- Hands Off: Avoid touching your face, as this can transfer bacteria from your hands to your skin, potentially causing breakouts.
- Cleanse After Exercise: If you exercise, wash your face and body promptly after your workout to remove sweat and oil that can clog pores.
- Diet and Hydration: Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit dairy and sugary foods, as they may contribute to acne in some individuals. Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques, as high stress levels can stimulate sebum production and worsen acne.
- Avoid Over-Exfoliating: While exfoliation is beneficial, overdoing it can irritate the skin and lead to more blackheads. Stick to the recommended exfoliation frequency for your skin type.
- Clean Pillowcases and Bedding: Regularly wash your pillowcases and bedding to prevent the accumulation of oil, dirt, and bacteria that can transfer to your skin.
- Avoid Heavy Hair Products: Use oil-free hair products and avoid applying them to your face. Heavy hair products can clog the pores on your forehead and hairline.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain skin health, so drink enough water throughout the day.
Remember that consistency is key when it comes to preventing blackheads. By understanding the causes, triggers, and prevention strategies, you can maintain clear and healthy skin while avoiding the temptation to squeeze blackheads.